Terraform reference
The Conduktor Terraform provider gives you the ability to perform some operations on Conduktor Console state directly from existing Terraform Infrastructure-as-Code environment.
You can also read about the provider on the Terraform Provider Page directly.
Conduktor Terraform Provider is currently in Alpha and doesn't support all the Conduktor resources yet. Get in touch if you have feedback or would like to be a design partner.
Install
The provider should be installed automatically with terraform init, however we recommend to pin a specific version or range of versions using the required_providers configuration:
terraform {
required_providers {
conduktor = {
source = "conduktor/conduktor"
version = "~> X.Y" # where X.Y is the current major version and minor version
}
}
}
Configure
To use the Conduktor Terraform Provider, you need to configure:
- the mode, since the provider can also be used for managing Conduktor Gateway resources,
- the URL of Conduktor Console,
- the authentication mechanism: either using an API key or the local user credentials (usually admin account)
View the full configuration reference.
Authenticate using API Keys
# configure provider
provider "conduktor" {
mode = "console"
base_url = "http://localhost:8080"
api_token = "your-api-key"
}
There are two types of API Keys: admin and Self-service application.
- Admin API Key
- Self-service Application API Key
Admin API Keys grant the maximum permissions on Console.
- CLI
- UI
# Generate a key named my-admin-key
$ conduktor token create admin my-admin-key
AWpw1sZZC20=.29Qb9KbyeQTrewMtnVDYAprxmYo7MUQats2KHzVhx+B/kGOBuIoH8CMsjOcvolUjLKFqbQNSvY0/98wb8mqxU4NwQTSgbSSAlLxau3caByHR6/X9EeqQdj3Lhf0xCzh87/GxYK5JG2DI1VWj55A6xcH++ottyG909PwuGe/GIwgfxX3FKaopg8hxgUmPJNRSWqX+75a8eQi014J4YxuTD7w+723kOQBTXOysfGUaYnfwCCjPPmSWXEEqy5wkH2NS+jXi3S6+fH0ts8CoqvV6Z8YLmBupdMgCtJ9MVBYeDarIzQw6XY7yNuypUqer0dcd9B3KyVR8ecNpFiF7ybvP4g==
Go to Settings > API Keys and select New API Key:
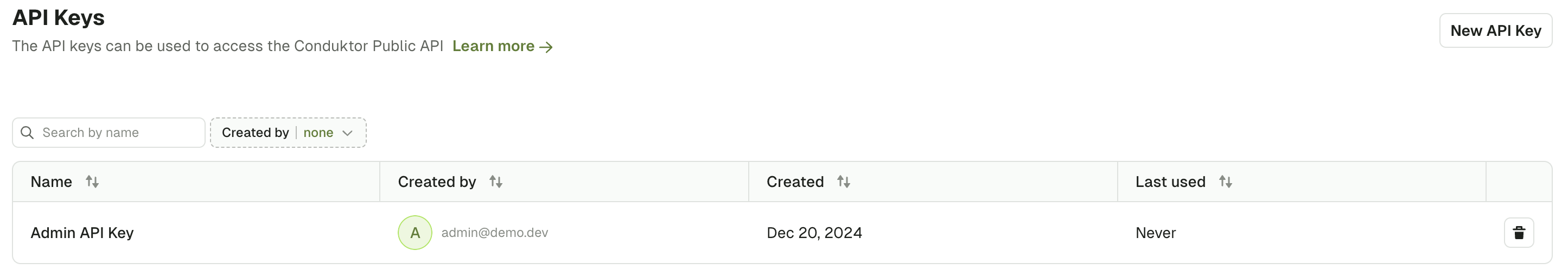
Self-service Application API Key permissions are limited to the scope of the ApplicationInstance for which they have been generated. Find out more about Self-service.
- CLI
- UI
$ conduktor token create application-instance -i=<my-app-instance> my-app-instance-key
AWpw1sZZC20=.29Qb9KbyeQTrewMtnVDYAprxmYo7MUQats2KHzVhx+B/kGOBuIoH8CMsjOcvolUjLKFqbQNSvY0/98wb8mqxU4NwQTSgbSSAlLxau3caByHR6/X9EeqQdj3Lhf0xCzh87/GxYK5JG2DI1VWj55A6xcH++ottyG909PwuGe/GIwgfxX3FKaopg8hxgUmPJNRSWqX+75a8eQi014J4YxuTD7w+723kOQBTXOysfGUaYnfwCCjPPmSWXEEqy5wkH2NS+jXi3S6+fH0ts8CoqvV6Z8YLmBupdMgCtJ9MVBYeDarIzQw6XY7yNuypUqer0dcd9B3KyVR8ecNpFiF7ybvP4g==
Go to Applications, pick your Application and under the Application Instances tab click New API Key:
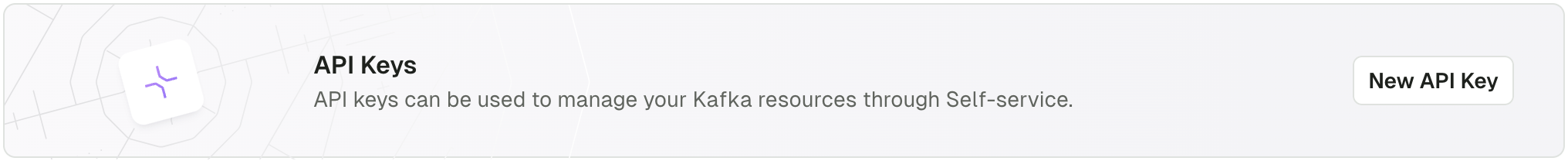
Authenticate using short-lived user credentials
This type of API Key will have the permissions of the user who created it. It only works for Local and LDAP users.
Short-lived user API Keys will be valid for the same duration as the configured session lifetime.
OIDC users can't be used.
# configure provider
provider "conduktor" {
mode = "console"
base_url = "http://localhost:8080"
admin_user = "console-admin@mycompany.io"
admin_password = "console-admin-password"
}
Environment variables
The provider configuration also supports environment variables for all attributes except for mode.
| Environment variables | HCL value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| n/a | mode | Terraform Provider mode: either console or gateway |
CDK_CONSOLE_BASE_URL | base_url | Console base URL, e.g. http://localhost:8080 |
CDK_API_KEY | api_token | Console API Key |
CDK_CONSOLE_USER | admin_user | Console user login email |
CDK_CONSOLE_PASSWORD | admin_password | Console user login password |
CDK_CONSOLE_CERT | cert | Cert in PEM format to authenticate using client certificates |
CDK_CONSOLE_INSECURE | insecure | Skip TLS verification flag. Defaults to false |
CDK_CONSOLE_CACERT | cacert | Root CA certificate in PEM format to verify the Conduktor Console certificate |
CDK_CONSOLE_KEY | key | Key in PEM format to authenticate using client certificates |
The configuration resolution is (in order of priority):
- HCL values
- Environment variables
- Default values (if applicable)
Provider usage
Once the provider is configured, all the currently available resources can be used in the Terraform definition.
Usage example
A full example of user and group creation using Conduktor Console locally is available on port 8080 with default admin account credentials admin@mycompany.io / admin_password.
# Provider installation configuration
terraform {
required_providers {
conduktor = {
source = "conduktor/conduktor"
version = ">= 0.4.0"
}
}
}
# Provider configuration
provider "conduktor" {
mode = "console"
base_url = "http://localhost:8080"
admin_user = "admin@mycompany.io"
admin_password = "admin_password"
}
# Create example_user, Bob
resource "conduktor_user_v2" "bob" {
name = "bob@mycompany.io"
spec = {
firstname = "Bob"
lastname = "Smith"
permissions = [
{
resource_type = "PLATFORM"
permissions = ["userView", "datamaskingView", "auditLogView"]
}
]
}
}
# Create a group with Bob as a member
resource "conduktor_group_v2" "example_group" {
name = "team-a"
spec = {
display_name = "team-a"
description = "The group of team-a"
members = [ conduktor_user_v2.bob.name ]
permissions = []
}
}
Then on a terminal with Terraform installed and in a directory containing conduktor-iac.tf file.
# Initialize terraform project
terraform init
# Plan to preview the changes Terraform will make to match your configuration.
terraform plan
# Apply to make the planned changes.
terraform apply
Now if you navigate to the Conduktor UI, you will see a new user, Bob, and team-a's group created.
Log in using an external SSO (LDAP or OIDC) with email bob@mycompany.io and you'll be recognized by Conduktor as being in the team-a group.
To revert the Conduktor state, you can destroy the created resources using terraform destroy. Find out more about Terraform CLI commands.
Case of the generic resource
The generic resource leverage the YAML format used by the CLI to be used as resource definition in Terraform.
This is an experimental resource that has several limitations and is subject to breaking changes in future releases.
Don't include it in your production workflows as this is unsupported.